Portfolio analysis undertaken by Vanguard demonstrates that private equity (PE) can play a significant role in strategic, long-term, diversified portfolios.
Vanguard highlight:
- Although private equity and public equity share some risk and return characteristics, there are key structural differences. (Both have a role to play in a well-diversified and robust portfolio.)
- Private equity investments are illiquid and so must be actively managed, introducing both illiquidity and manager specific risk to the multi-asset portfolio.
- Conventional asset allocation approaches such as mean-variance efficient frontiers omit illiquidity and active risk dimensions from the risk-return trade-off.
- Asset allocation models that do not reflect the unique aspects of PE tend to over allocate to PE and therefore introduce unintended risks into a multi-asset portfolio.
In this Research Paper Vanguard introduce a new portfolio construction framework that accounts for private equity’s risk and return characteristics, Vanguard Asset Allocation Model (VAAM).
They conclude that there is no single recommended allocation for all investors. “Private equity allocations depend on each investor’s specific set of circumstances, such as the degree of risk tolerance, including active risk tolerance, and the ability to find and access high-quality managers.”
In allocating to PE investors must carefully consider their willingness and ability to handle a long-term lack of liquidity, constraints on rebalancing, and uncertainty around the timing and size of cash inflows and outflows.
Below is a summary of the Vanguard Research Paper, which also draws on this All About Alpha article by Vanguard.
The Vanguard paper addresses the following three main issues:
- Complexity in the structure and mechanics of PE that lead to unique sources of risk and return versus public equity investments.
- Data limitations due to lack of standardized publicly available marked-to-market performance reporting.
- Lack of portfolio construction frameworks that can appropriately account for PE’s unique characteristics.
Why returns from Private Equity are different to those from Public Equities
For those new to PE the Vanguard paper provides an excellent introduction, including topics such as what is a PE investment, the growth in PE over the last two decades, and how to access PE.
Their discussions on identifying the drivers of PE returns is very good.
Vanguard outline four key reasons why the economic returns of private equity should be different than those of public equity benchmarks:
Liquidity premium.
“Investors in private equity have less ability to trade their investment and do not control the timing or size of cash flows if invested in funds; therefore, they should require compensation in the form of a liquidity premium.” Returns from the “Liquidity Premium” vary over time.
An important point in relation to liquidity, is that most long-term investors do not need a 100% liquid portfolio. Most investors over-estimate their liquidity needs (this is not to minimise the importance of portfolio liquidity).
Vanguard note there are two different but related forms of liquidity risk:
- Market liquidity risk – the ease with which an investment can be traded.
- Funding liquidity risk – investors must be flexible enough to make contributions quickly and to deal with potential material delays in distributions from the PE funds
Other risk factors
“The average characteristics of private equity companies may be different than those of public companies (for example, industry, size, financial leverage, geography, and valuation).”
There is a large body of research that attempts to estimate the common risk factors of PE, such as size and value.
Vanguard provides results from a sample of academic studies which suggests PE Funds tend to have above market risk (high betas) and a small size tilt. The research also suggests that buyout funds have a value bias, whereas venture capital funds display a negative value bias.
These are important considerations to contemplate when evaluating the inclusion of PE into a diversified and robust portfolio to minimise unintended risk exposures.
Manager-specific alpha
“Investors accept idiosyncratic manager-specific risk in exchange for the opportunity to generate alpha.”
Vanguard outlined that PE managers look to add value in the following ways:
- Company selection. In addition to their company selection skills, some managers may have access to certain deals or parts of the market that others may not because of their reputation or skill set.
- Thematic bets. Managers can choose to focus on secular or structural changes (such as technological, regulatory, and consumer preference) that may not be fully reflected in company valuations today.
- Governance. PE firms can provide the oversight to help portfolio companies with the likes of strategic planning, conflicts of interest, and remaining focused on competitive advantages.
- Finance. PE firms provide guidance in optimising capital structures of portfolio companies.
- Operations. PE firms may have specific sector or industry expertise that can help portfolio companies make key decisions, reduce costs, and identify growth opportunities.
Manager due diligence is always important, in relation to PE investors should understand how a manager seeks to add value, why the manager believes they will be successful, and what success will look like.
Always have a set of expectations as to a manager’s expected performance, these can be both quantitative and qualitative. Undertake ongoing monitoring and review of the manager relative to these expectations.
As the Vanguard article highlights “David Swensen, the long-time chief investment officer of the Yale University endowment who may be the most well-known evaluator of private equity managers in the world, stresses that qualitative factors (such as people and process) play a central role in manager evaluations.”
All-in costs
Vanguard make the very significant point “Investors care most about performance net of all costs.”
The size and structure of PE fees/costs are materially different to investing into Public markets. Investors will need to understand these and most importantly assess the likely performance outcome after all fees and charges.
Private Equity Portfolio modelling challenges
Most asset allocation models are built with liquid public assets in mind (e.g. public equities, fixed income, and cash) and assume the portfolio can be rebalanced periodically and with minimum cost.
However, with the introduction of illiquid asset classes, such as PE, there are some fundamental differences that need to be accounted for when undertaking portfolio modelling.
As outlined by Vanguard, these include:
- Smoothed (appraisal-based) private equity return estimates: Private equity historical return data have limited holdings transparency and are based on subjective appraisal-based valuations rather than observable, transaction-based prices on a public exchange. Relying solely on appraisal-based values to calculate returns can lead to significant underestimation of the volatility of returns.
- Illiquidity and frictionless rebalancing: Investors in private equity have less ability to trade their investment and rebalance their portfolio back to the intended target allocation. For this reason, they should require compensation in the form of a liquidity premium.
- Uncertainty in timing and magnitude of cash flows: Because private equity investors cannot control the timing or size of private equity fund cash flows, they incur an additional type of risk.
- Illiquidity and valuation adjustment: Private equity fund investments cannot easily be accessed and liquidated unless at a discount to NAV in most cases. This implies that liquid asset prices and private equity fund NAVs are not directly comparable.
Therefore, there are three distinct sources of risk when investing into PE:
- Market Risk (Systematic risk) which Public Equities also have, and is best measured via decomposition of risk factors (e.g. value and small cap) that are present in the public markets. This risk is more accurately estimated after unsmoothing the returns from PE.
- Illiquidity factor risk that is unique to private equity and not observed in public markets.
- Manager (Idiosyncratic to the manager and unsystematic risk of individual companies) risk for the specific manager(s) selected. This is effectively active risk, with the potential to generate excess returns for the risk taken (which is alpha, a great portfolio diversifier).
Portfolio modelling with the inclusion of Private Equity
One of the key issues to consider when incorporating unlisted assets, such as PE, into a portfolio is the smoothed nature of the historical return data, which reflects appraisal-based valuations.
The use of smoothed historical returns results in an underestimation of return volatility. The underestimation of volatility could lead to an overallocation to PE when undertaking portfolio modelling.
For portfolio modelling purposes, the true underlying risk profile of PE needs to be understood to make a better assessment when comparing and combining with public market assets.
As Vanguard highlight, several “statistical methods have been proposed in the academic literature over the last few decades to try to better understand historical performance. None of them are without shortcomings, which is why there remains no universally agreed-upon approach among academics or practitioners.”
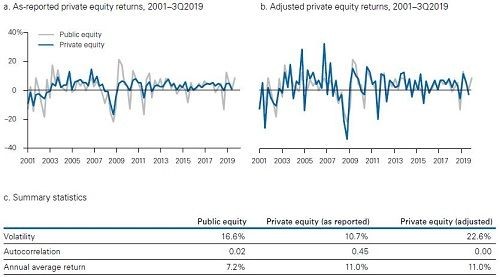
Vanguard follow a time-series technique to “unsmooth” historically reported PE returns. For a more in-depth discussion please see the Research Paper.
The adjustment to PE returns is presented in the Table below. Note how Private Equity (adjusted) volatility is 22.6%, up from 10.7% calculated using reported historical PE returns.
The adjusted PE returns results in a more realistic return profile for PE which can be used for portfolio modelling purposes, resulting in more sensible volatility and covariance estimations. Note historical PE returns have been preserved, only volatility measures have been adjusted.
In addition to estimating unbiased PE return estimates, as above, Vanguard also undertake the following adjustments to the standard portfolio modelling approach to address the issues identified above:
Account for the illiquidity of PE
Vanguard’s portfolio model, VAAM, drops the assumption of low cost and regular rebalancing assumed in standard portfolio modelling frameworks. Therefore, they assume that PE can not be fully rebalanced. As they note, “This illiquidity-constrained rebalance feature provides a more accurate representation of the risk-return trade-offs between liquidity premium and risks associated with private equity assessed within the portfolio optimization.”
Explicitly modelling private equity cash flows
Accounting for the uncertainty in timing and magnitude of PE cashflows Vanguard explicitly model cashflows in a multi-asset portfolio. As noted above, cash needs to put aside for future committed investments (contributions) and timing of distributions (capital returned) also needs to be accounted for.
It is important to note, this nature of PE leads to additional decision making in the management of a multi-asset portfolio that includes PE i.e. where cash tagged for future PE investment should be invested in the interim and decisions around portfolio rebalancing.
Optional valuation adjustment of the illiquid wealth of the portfolio
Vanguard also make an adjustment for the disparity in market value of liquid and illiquid assets. This reflects that illiquid assets, such as PE, can at times be sold in a secondary market, which more often than not trades at a discount (i.e. lower price) to asset values.
The discount function they implement “effectively converts illiquid wealth into its liquid equivalent.”
The Results
Compared to a multi-asset portfolio of 70% Equities and 30% Fixed Income (70/30) the key results include:
- Portfolio modelling that ignores private equity’s illiquid characteristics as covered above leads to a higher allocation in PE compared with Vanguard’s enhanced framework (VAAM)
- VAAM results in the PE allocation within “Equities” to fall from 50% to 30%
- The sensitivity to key risk parameters include: expectations the manager will generate lower excess returns results in a lower allocation (12% vs 23%); a “lower risk” manager results in a higher PE allocation (36% vs. 23%)
- For more conservative portfolios, such as a 30/70, although the total equity allocation decreases, the target PE share of total equity does not change materially relative to that of the 70/30 investor.
Please read my Disclosure Statement